Machineboy空
Object-Oriented Data Structures # WEEK01 : C++ variable, Class,Libraries 본문
Object-Oriented Data Structures # WEEK01 : C++ variable, Class,Libraries
안녕도라 2024. 1. 30. 10:531.1 C++ Introduction
two types of variable that we can have in C++
- Primmitive (6): common primitive types in C++
- int : stores integers
- char : stores single characters/single byte
- bool : stores a Boolean (T/F)
- float. : stores a floating point number
- double : stores a double-precision floating point number
- void : denotes the abseneces of a value
- User-defined (2) :
- string : secquence of characters
- vector : dynamically-growing array
how to start C++ program
By. the C++ standard, the starting point is a function.
- int main()
- if the program was successful, return value of main is 0
- fail, non-zero on errors
Which really powerful at C++ is when we start our own custom data type
1.2 C++ Classes
C++ classes encapsulate ( associate) data and associated functionality into an single object.

- In C++, data and functionality are seperated into two seperate protections: public and private.
- public members can be accessed by (anyone) client code.
- private members cannot be accessed by client code(only used within the class itself)
- In C++, the interface(.h file) to the class is defined seperately from the implementation(.cpp file)
- header file(.h) defines the interface to the class, which includs
- declaration of all member variables
- declaration of all member functions
- header file(.h) defines the interface to the class, which includs


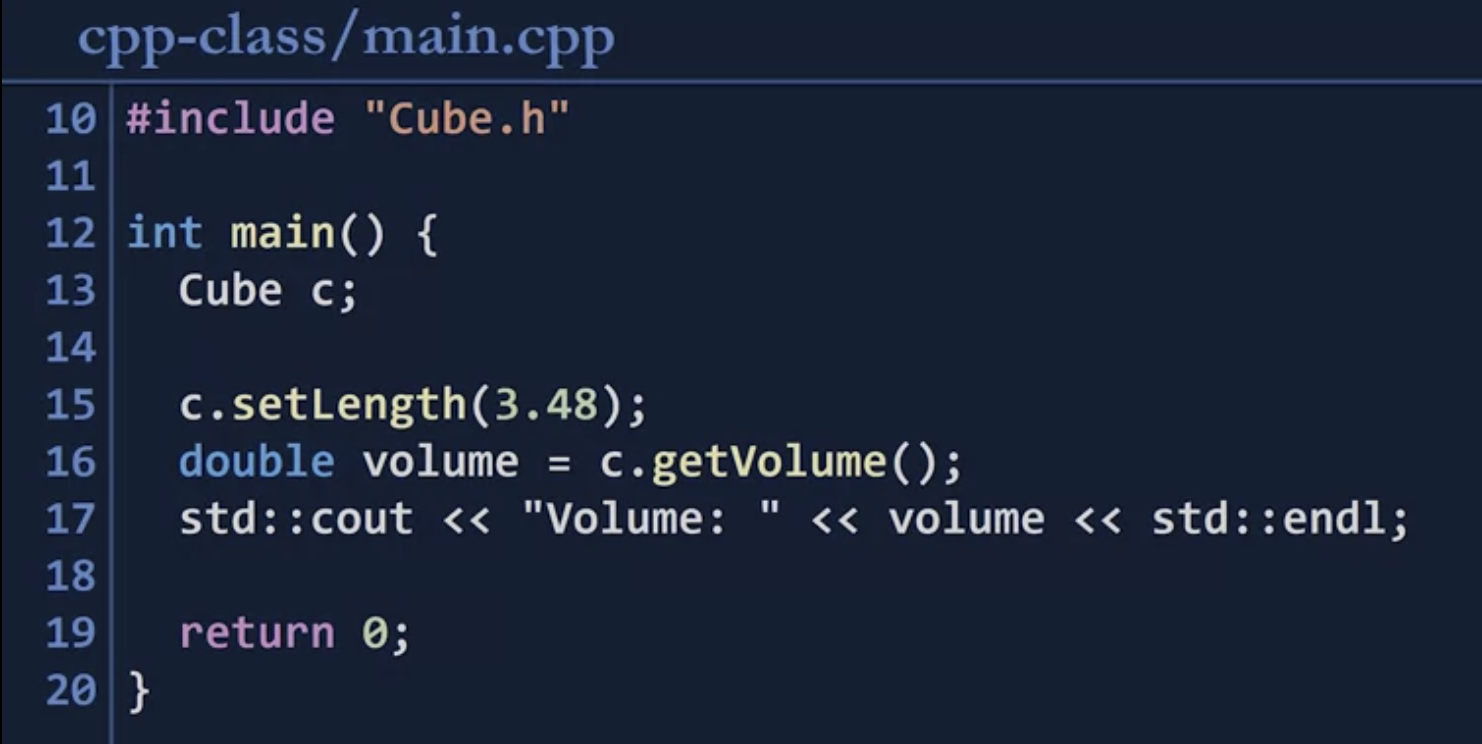
1.3 C++'s Standard Library(std)
C++ standard library (std or stl, standard template library)
provides a set of commonly used functionality and data structures to build upon.
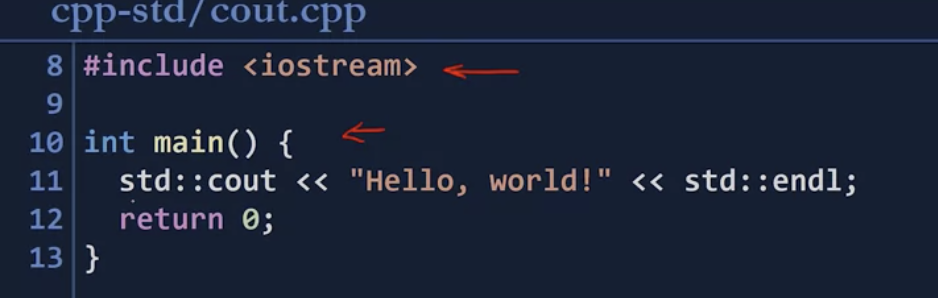
- iostream
- iostream header includes operations for reading/writing to files and the console itself
- including std::cout
- iostream header includes operations for reading/writing to files and the console itself

Namespaces allow us to avoid name conflicts for commonly used names.
if a feature from a namespace is used often, it can be imported into the global space with using:
매번 std::를 쓰기 싫다면
generally, good to minimize using keyword,
'using'makes less clear what you exactly write.
# using

A "cube" is rather generic-hundreds of cube-based data structures exist!
We will be specific about our Cube and specify that our CUbe is within the uiuc namespace;
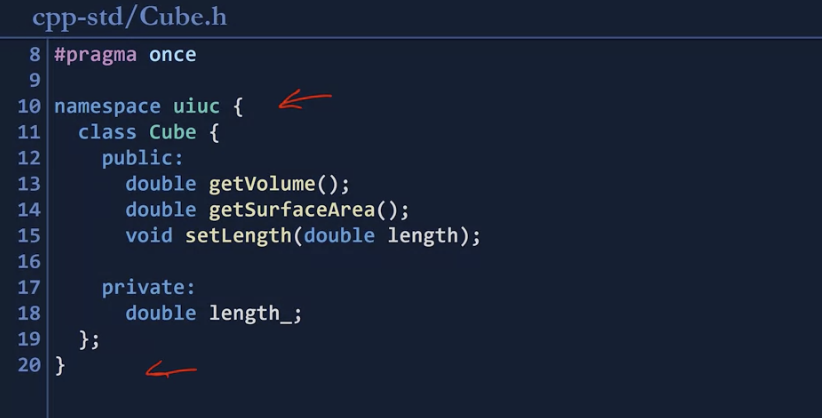
'Computer > 자료구조' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Object-Oriented Data Structures # WEEK03 : Constructors - default, copy & copy assignment operator (1) | 2024.02.02 |
|---|---|
| Object-Oriented Data Structures # WEEK02 : Heap Memory (0) | 2024.02.02 |
| Object-Oriented Data Structures # WEEK02 : Stack memory & Pointers (1) | 2024.01.31 |
| 값에 의한 호출 (call by value) vs 참조에 의한 호출(call by reference) (1) | 2024.01.15 |
| C++ 자료구조 종류 및 개요 (0) | 2024.01.15 |


